Thermal Design
// Early detection of potential design weaknesses.
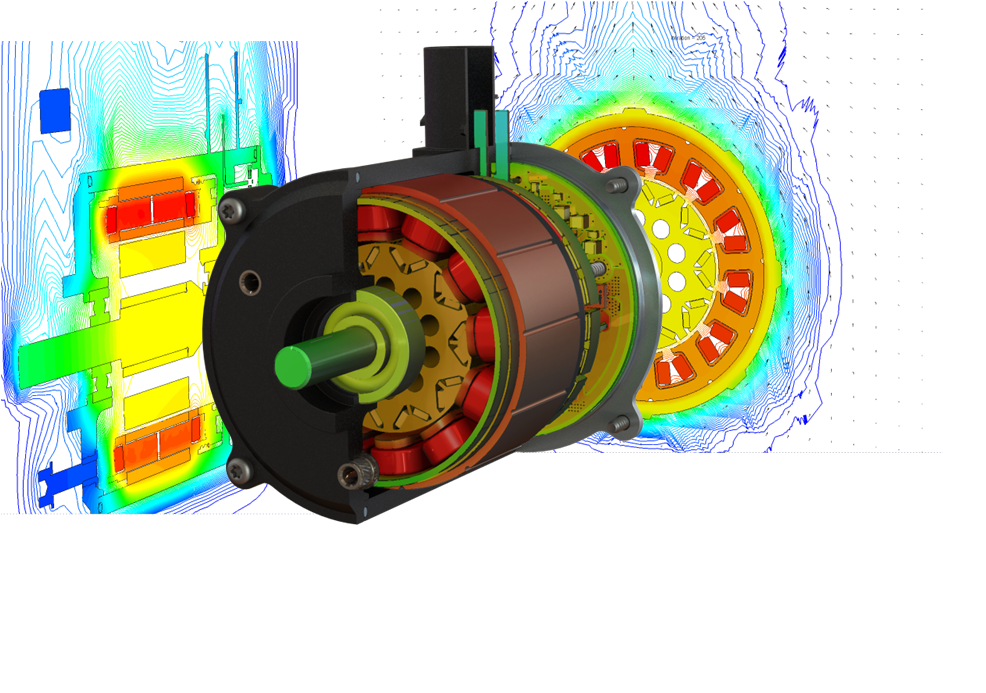

System analyses by means of CFD simulations

The increasing use of efficient PMSM or BLDC drive systems lead to more and more compact and highly integrated systems. For the coherent unit of motor and control electronics heat dissipation plays an important role, because it can make a major contribution to the fail-safety of the components or the entire system.
In this context, knowledge of the heat loss and the quality of the heat dissipation paths is still of great importance in the design phase. As a result, design adjustments can be made at an early stage and checked again by thermal simulation.
A thermal simulation offers the advantage of obtaining meaningful information about the heat distribution in the system with existing design data (CAD model) and sufficient knowledge about power losses, ambient conditions and load conditions.
Your benefits at a glance

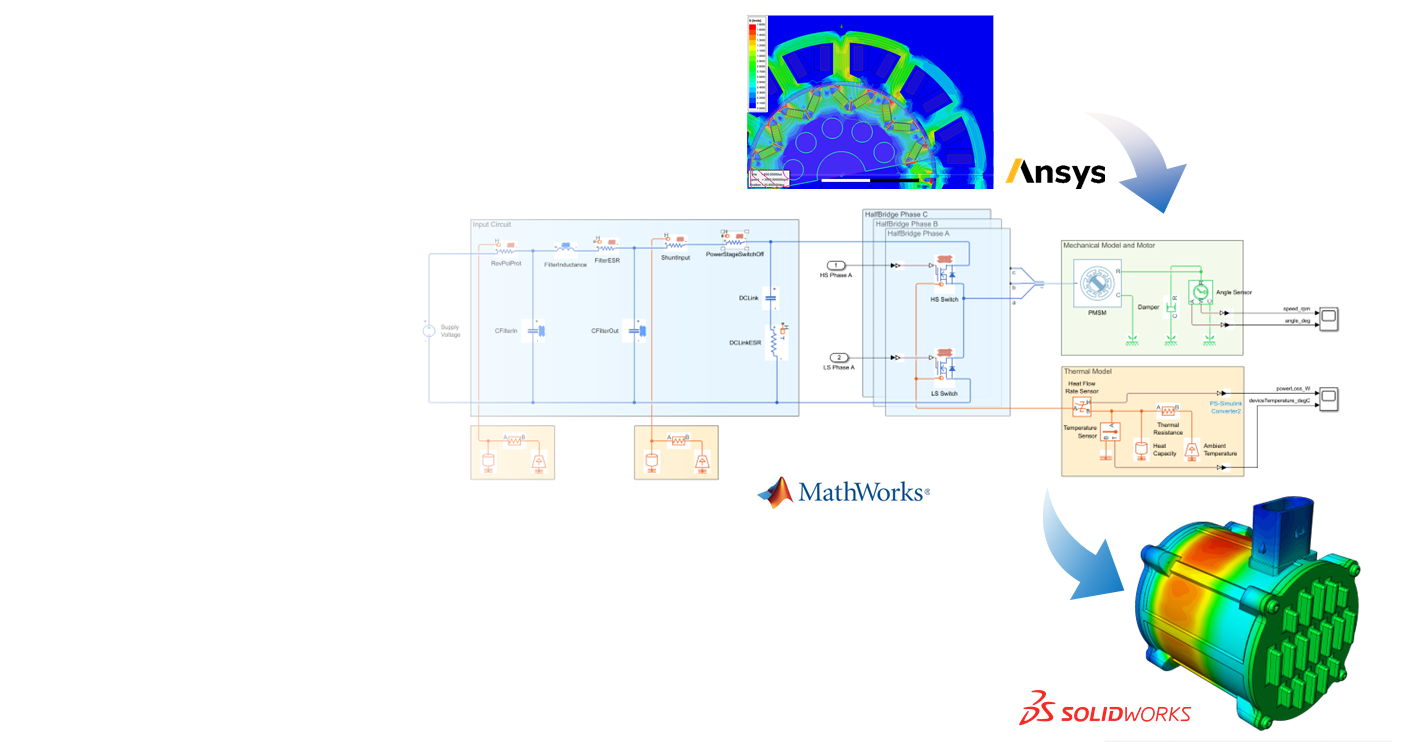
Model-based system approach
- Determination of motor parameters using magnetic circuit simulations based on Ansys Maxwell
- Processing of the motor parameters in a common system network model using MATLAB and Simscape
- Simulation of the system behavior for selected load points and thermal conditions
- Extraction of the power losses for further processing in the CFD flow simulation environment

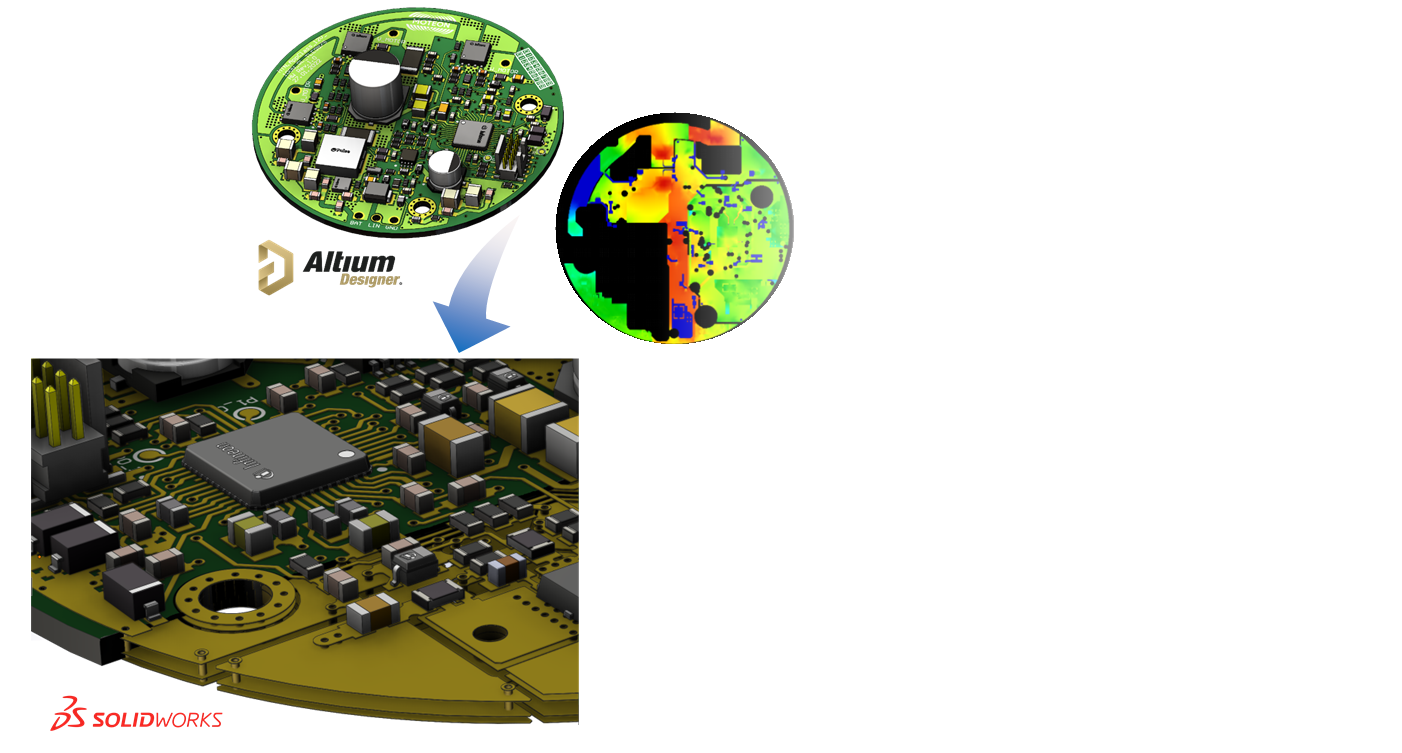
Electronics modeling
- ECAD and MCAD tool enables the exchange of detailed PCB models
- PCB models include inner and outer layers, solder mask and vias and the associated components
- Pre-simulated power losses can be applied to all relevant components
- Losses in the conduction paths can also be taken into account by using Altium PDN Analyzer

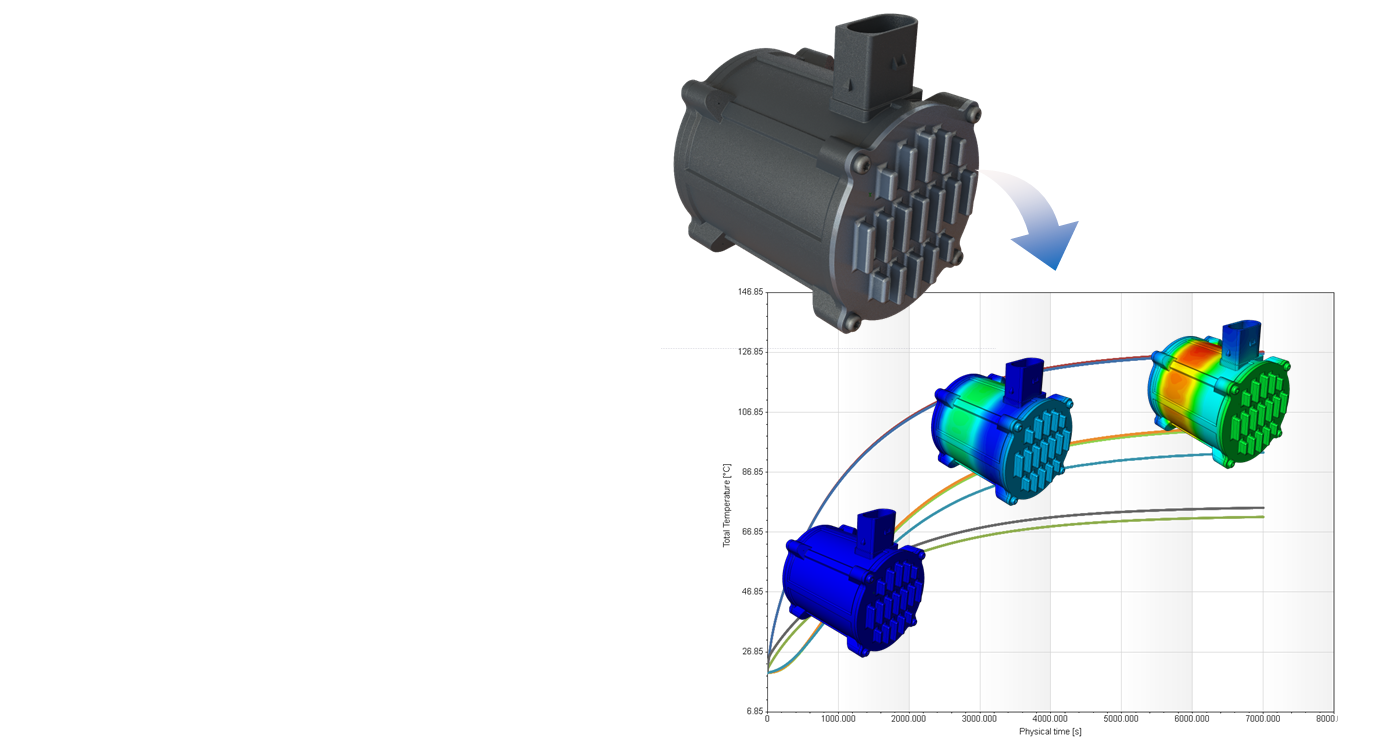
Transient simulation
- Temperature transitions can be simulated as a function of time up to a steady state temperature so that time constants can be determined for further simulations
- Use of load profiles, e.g. to simulate the switch-on/switch-off or partial load behavior
- Simulation of specific situations by changing the ambient conditions as a function of time
- Simulation of rotatory or translational motion sequences, e.g. to consider influences of heat distribution effects